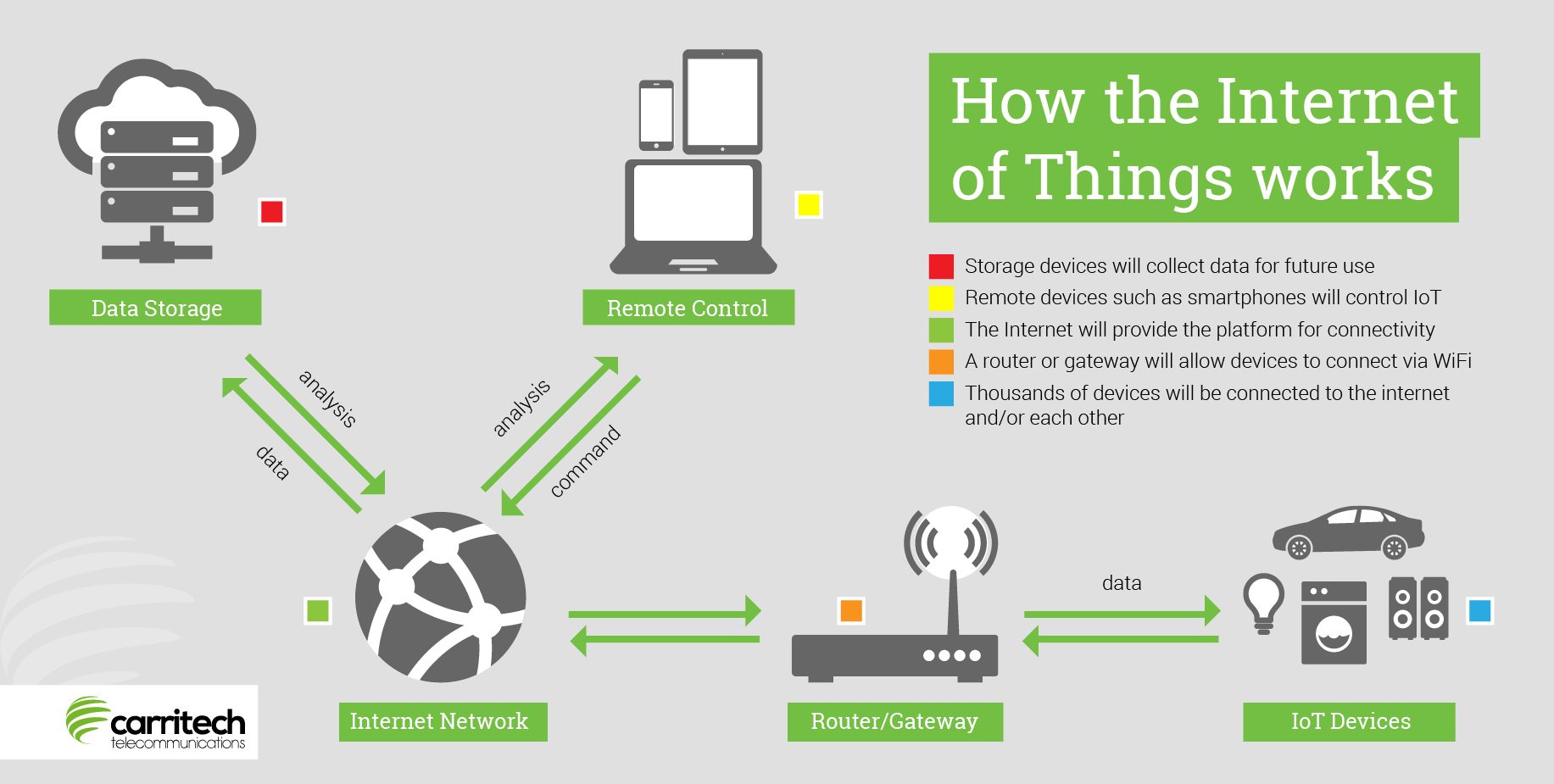
The Internet, the backbone of modern communication, relies heavily on efficient data transmission to enable the smooth exchange of information across global networks.
But have you ever wondered how data travels across the vast expanses of the digital world? This article explores the mechanisms that allow data to move across the internet seamlessly.
1. Data Transmission Basics: Understanding the Journey
When you send or receive information over the internet — whether browsing websites, streaming a video, or sending an email — the data is broken down into small chunks known as packets.
These packets traverse various network infrastructures before reaching their destination. Understanding how this process works starts with recognizing a few fundamental components of data transmission:
- Data Packets: Data isn’t sent as a whole file or message. Instead, it’s chopped into smaller units called packets, making it more manageable and enabling faster transmission. These packets contain part of your data along with important information such as the destination address and sequence number, ensuring they arrive intact.
- Packet Switching: This method allows the internet to be robust and efficient. Packet-switching refers to how packets take different paths from the sender to the recipient, depending on the available network routes at that moment. It ensures that the data reaches its destination even if certain parts of the network are congested or damaged.
2. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) & Internet Protocol (IP)
To ensure data transmission occurs accurately and efficiently, two key protocols play a central role: the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP).
- Internet Protocol (IP): IP is responsible for addressing and routing data. When you send data, the system first assigns it an address (your IP address), which helps network devices know where to send the packets. It’s similar to a postal address, directing each packet to the correct destination on the internet.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): Once data packets are sent to their destination, the TCP ensures they are correctly received and reassembled. If some packets are lost during transmission, the TCP requests them to be sent again, ensuring accurate delivery.
Together, TCP/IP acts as the “language” of the internet, ensuring that data packets are sent, received, and reconstructed in their original form.
3. The Role of Routers and Switches
As packets travel through the internet, they must go through devices known as routers and switches. Routers guide the packets on their journey, determining the best path through the network based on the most efficient routes.
Switches, on the other hand, are responsible for directing the packets within a local network, ensuring that packets reach their correct endpoint.
These network devices work together, forming a “map” of how the data should flow across the internet. They manage traffic to avoid bottlenecks and to optimize how efficiently the internet functions.
4. The Layered Approach: OSI Model
Data transmission also depends on structured, layered communication protocols. One widely adopted model is the OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection), which divides communication tasks into seven layers:
- Physical Layer: Transmitting raw bits over a physical medium like cables, fiber optics, or wireless channels.
- Data Link Layer: Manages how data is transferred between devices within the same network, ensuring error-free communication.
- Network Layer: The internet protocol (IP) comes into play, determining the route and destination of data across multiple networks.
- Transport Layer: Ensures data is transmitted in complete and ordered packets, where TCP takes charge.
- Session Layer: Maintains continuous data exchange during the transmission process.
- Presentation Layer: Formats and encrypts data to ensure that the content is readable by the recipient.
- Application Layer: This is where end-user applications, such as browsers and email clients, reside and interact with data.
Together, these layers ensure efficient data transmission, from the raw bit level to a meaningful file download or webpage display.
5. The Path to Your Device: The Role of DNS Servers
Every time you type a website address into your browser, you might not realize that a hidden process occurs behind the scenes. A Domain Name System (DNS) Server translates that human-readable address (like www.example.com) into an IP address that computers understand. This critical translation ensures that you are connected to the correct server hosting the information you requested.
DNS acts as a directory that ensures every data packet sent on the internet reaches the correct website or service.
6. Wireless and Wired Communication
While traditional data transmission has been carried out through wired connections, much of today’s internet data transfer takes place over wireless networks.
Devices can connect using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or mobile networks (such as 4G and 5G). These wireless technologies allow data to be transmitted through electromagnetic waves, but they still depend on the same fundamental principles that govern wired communication, like packet switching and IP addressing.
7. The Importance of Data Transmission Speed and Latency
Two additional factors critical to the success of internet data transmission are speed and latency. Speed refers to the rate at which data can be transmitted, usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
Latency, on the other hand, is the time delay between sending a packet and receiving a response. Optimizing both speed and latency is essential for providing smooth user experiences in activities such as streaming, gaming, and video conferencing.
Conclusion
Understanding how data is transmitted over the internet involves a multi-layered system of protocols, infrastructure, and processes.
From the initial breakdown of data into packets to the final reassembly on the destination device, each step plays a role in ensuring data is delivered accurately and efficiently.
By utilizing a complex combination of packet-switching, TCP/IP protocols, routing devices, and the OSI model, the internet remains an interconnected and powerful tool that fuels modern communication.
With every action you take online, the inner workings of data transmission quietly take place, making sure you’re always connected, informed, and ready to explore the digital world. For more Internet Marketing information check the internetgainer.